Hip joint replacement
| Normal anatomy |
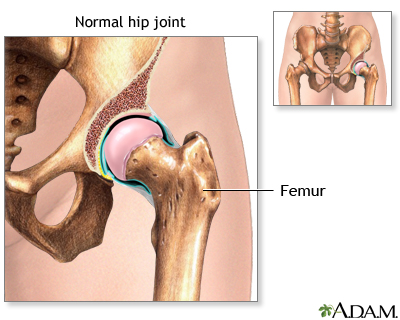 |
| Indications |
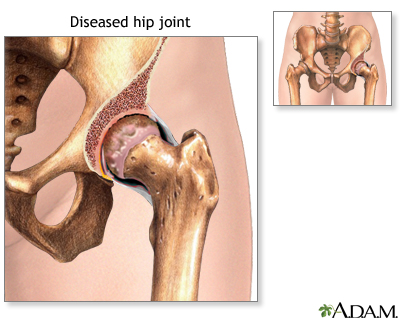 Hip joint replacement, or total hip replacement, is surgery to replace all or part of the hip joint with an artificial device (a prosthesis) to restore joint movement and reduce pain. Total hip replacement is mostly done in older people. The operation is usually not recommended for younger people because of the strain they can put on the artificial hip. The indications for the replacement of the hip joint include:
This surgery is not recommended for patients who have:
|
| Procedure, part 1 |
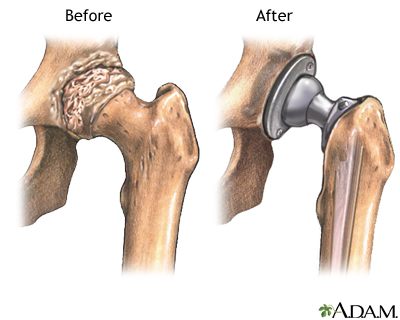
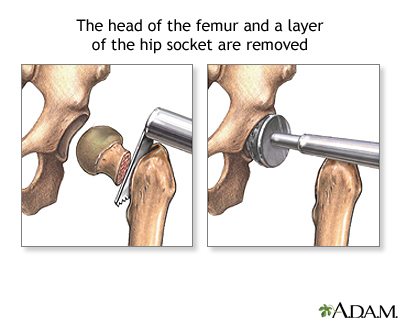 The hip is a ball and a socket joint, linking the ball at the head of the thigh bone (femur) and the cup in the pelvic bone. A total hip prosthesis is surgically implanted to replace the damaged bone within the hip joint. The total hip prosthesis consists of three parts:
If a hemi-arthroplasty is performed, either the femoral head or the hip socket (acetabulum) will be replaced with a prosthetic device. You will receive an extensive pre-operative evaluation of your hip to determine if you are a candidate for a hip replacement procedure. Evaluation will include assessment of the degree of disability and impact on your lifestyle, pre-existing medical conditions, and an evaluation of heart and lung function. The surgery will be performed using general or spinal anesthesia. The orthopedic surgeon makes an incision along the affected hip joint, exposing the hip joint. The head of the femur and the cup are cut out and removed. |
| Procedure, part 2 |
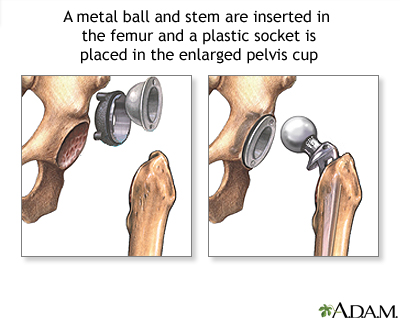 Then a metal ball and the metal stem is inserted in the femur (thigh bone) and a plastic socket is placed in the enlarged pelvis cup. The artificial components are fixed in place (sometimes a special cement is used). The muscles and tendons are then replaced against the bones and the incision is closed. You will return from surgery with a large dressing to the hip area. A small drainage tube will be placed during surgery to help drain excess fluids from the joint area. |
| Aftercare |
 You will experience moderate to severe pain after surgery. However, patient-controlled analgesia (PCA), intravenous (IV), or epidural analgesics are effective in controlling post-operative pain. The pain should gradually decrease, and by the third day after surgery, oral analgesic medications may be sufficient to control your pain. Try to schedule your pain medications about one half hour before walking or changing position. Results with a hip prosthesis have been excellent. The operation relieves pain and stiffness symptoms, and most patients (over 80%) need no help walking. With time, loosening of the artificial joint may occur because of the limited properties of the cement used to attach the artificial parts to the bones. You will remain in the hospital for up to a week after surgery. The use of crutches or a walker is necessary at the start of rehabilitation. However, some people may need further rehabilitation and assistance after hip replacement surgery. Temporary placement in a rehabilitation unit or long-term care center may be necessary until mobility has improved and the person can safely live independently. These centers will provide intensive physical therapy to assist in regaining muscle strength and flexibility in the joint. Positioning is very important after surgery to reduce stress on the new joint and displacement of the joint. The new hip will not have the same range of movement of the original joint, although you should eventually be able to return to your previous level of activity. However, you should avoid vigorous or high impact sports, such as skiing or contact sports. SPECIAL PRECAUTIONS: The new joint has a limited range of movement. Until your joint has healed, you will need to take special precautions to avoid dislocation of the joint, including:
|
|
Review Date:
12/22/2011 Reviewed By: Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |

