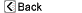TURP
| Normal anatomy |
| The prostate gland is an organ that surrounds the urinary urethra in men. It secretes fluid that mixes with the sperm to make semen. |
| Indication |
|
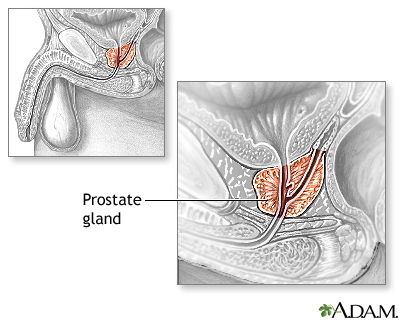
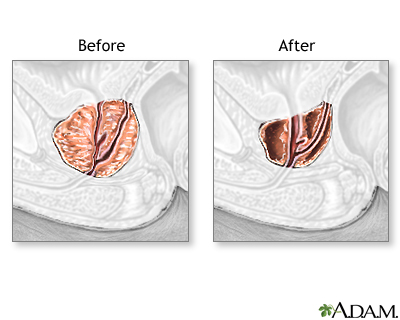
An enlarged prostate gland compresses the urethra, causing problems with urination. Prostate enlargement is caused by prostate gland overgrowth (benign prostatic hyperplasia, or BPH) or in some cases, prostate cancer. |
| Procedure |
|
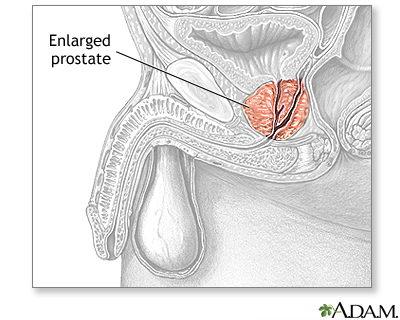
With an anesthetic (general anesthetic or spinal), a special instrument, called a resectoscope is inserted through the urethra into the prostate. The resectosope is used to remove the blocking portions of the prostate. Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) is the most common type of surgical procedure for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Newer, less invasive procedures are gaining favor, and medications allow many men to avoid surgery. |
| Aftercare |
|
TURP is typically successful at reducing the symptoms of an enlarged prostate. |
|
Review Date:
12/22/2011
Reviewed By:
Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Senior Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.