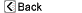Craniotomy
| Normal anatomy |
| The brain is located inside the cranium. The cranium is a set of bones which makes up the skull, and protects and holds the brain. |
| Indication |
Brain surgery may be needed to treat:
- Brain tumors
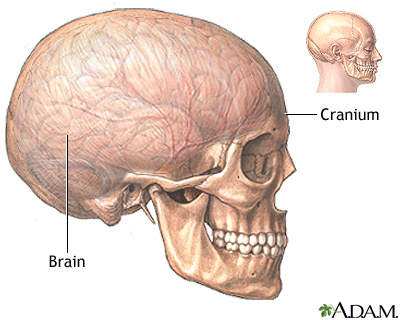
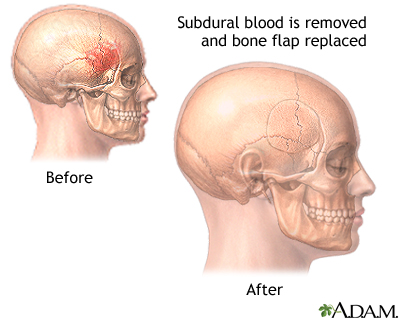
- Bleeding (hemorrhage) due to stroke or trauma or blood clots (hematomas) from injuries (subdural hematoma or epidural hematomas)
- Weakness in an artery wall (cerebral aneurysms)
- Damage to tissues covering the brain (dura)
- Pockets of infection in the brain (brain abscesses)
- Severe nerve or facial pain (such as trigeminal neuralgia or tic douloureux)
- Epilepsy
|
| Procedure |
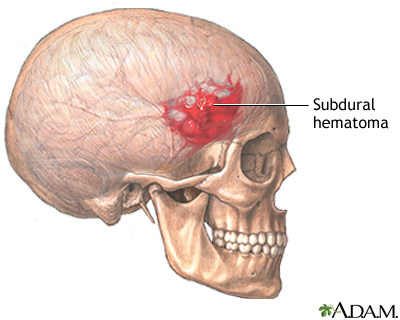
| The hair on part of the scalp is shaved. An incision is made through the scalp and a hole is drilled through the skull. A piece of the skull may be removed while the brain is being operated on and replaced before the skin is stitched closed. The surgery in which the brain is accessed through the skull is called "craniotomy". |
| Aftercare |
| The results depend on the source, severity, and location of the problem. |
|
Review Date:
12/22/2011
Reviewed By:
Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.