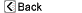Carotid artery surgery
| Normal anatomy |
There are two carotid arteries, one on each side of the neck. In turn, the left and right carotid arteries each branch into an internal and external division. The carotid arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the head and brain.
|
| Indications |
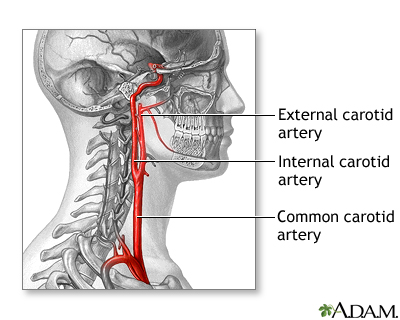
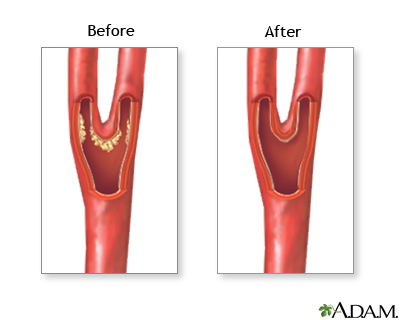
When the carotid arteries become blocked with cholesterol plaques (atherosclerotic plaques), blood flow to the brain is compromised. Also, small pieces of plaque can break off and block small arteries in the brain. This blockage of the blood vessels can cause transient-ischemic attacks and strokes.
|
| Procedure |
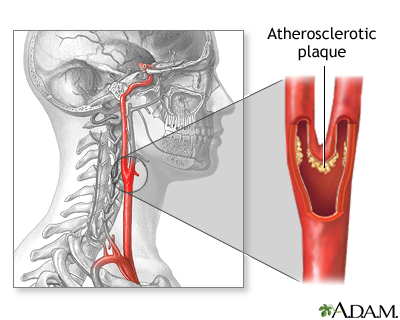
While you are deep asleep (under anesthesia) and pain-free, an incision is made in the neck, over the blocked carotid artery. A tube is inserted above and below the blockage to temporarily re-direct the blood flow. Fat and cholesterol build-ups are removed from the carotid artery (endarterectomy). The artery is stitched (sutured) closed, the tube is removed, and the incision is closed.
|
| Aftercare |
A normal hospital stay is 1 - 3 days after surgery. Avoid bending the neck sharply in any direction.
|
|
Review Date:
12/22/2011
Reviewed By:
Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.