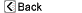Colon cancer
| Normal anatomy |
| The colon, or large intestine, is a muscular tube that begins at the end of the small intestine and ends at the rectum. The colon absorbs water from liquid stool that is delivered to it from the small intestine. |
| Indication |
|
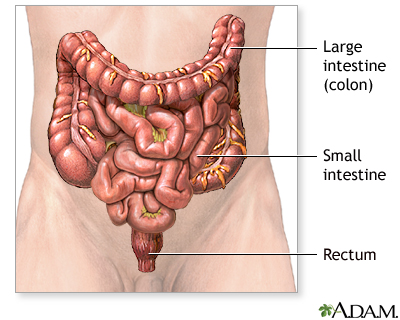
Colon cancer is the third most common internal cancer in the United States. Risk factors include certain types of colonic polyps, inflammatory bowel disease (such as Crohn's disease or ulcerative colitis), and certain hereditary disorders. Obesity, lack of exercise, and poor diets also contribute to colon cancer. |
| Incision |
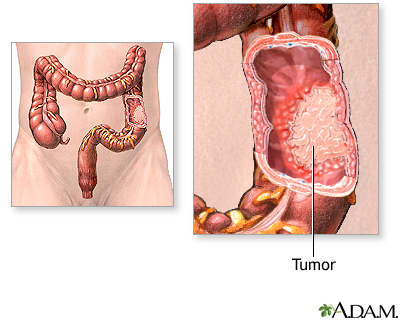
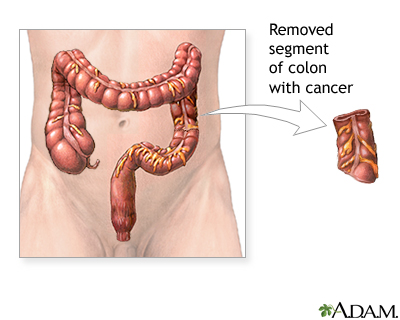
| The treatment of colon cancer depends on the stage of the disease. Stage I cancer is limited to the inner lining of the colon; stage II cancer involves the entire wall of the colon; stage III cancer has spread to the lymph nodes; stage IV cancer has spread to other organs (metastasized). |
| Procedure |
| Surgery is the main treatment for colon cancer, and removal of the involved colon is required. If the cancer is located near the rectum, a colostomy may be necessary.
For stage I and II colon cancer, surgery is usually the only treatment.
For stage III or IV colon cancer, chemotherapy is necessary after surgery. There is also some suggestion that chemotherapy may also be helpful in some selected stage II patients. Chemotherapy involves a course of drugs which are toxic to cancer cells.
|
| Aftercare |
|
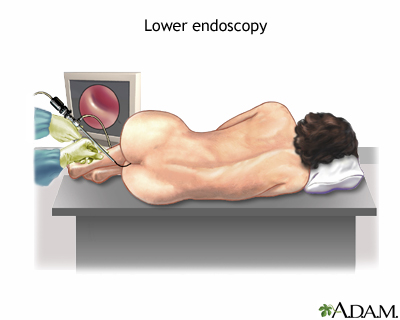
Stage I and II colon cancer have very high cure rates (60 - 90%); lower cure rates are seen with stage III and IV colon cancer. To detect colon cancer early, when it is most curable, everyone over the age of 50 should have regular screening for colon cancer. Colonoscopy is the most accurate screening test. |
|
Review Date:
5/14/2012
Reviewed By:
Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.