Atherosclerosis of internal carotid artery
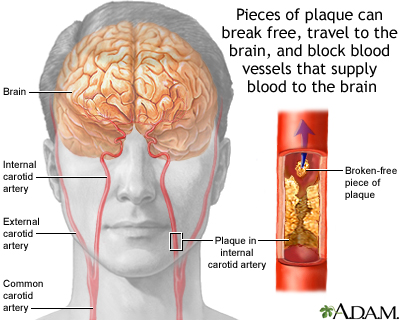
The build-up of plaque in the internal carotid artery may occasionally lead to narrowing and irregularity of the artery's channel, preventing proper blood flow to the brain. Sometimes, pieces of plaque in the internal carotid artery can break free, travel to the brain, and block blood vessels that supply blood to the brain. The most common complication of severe narrowing is the formation of clots on the fatty plaques. If the clots break free and travel to the brain, they can cause a stroke, with possible paralysis or other deficits.
|
Review Date:
12/26/2011 Reviewed By: Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Senior Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.

