Antibodies
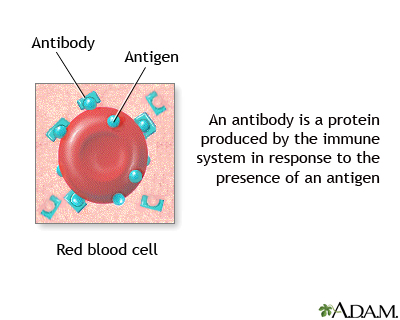
Antigens are large molecules (usually proteins) on the surface of cells, viruses, fungi, bacteria, and some non-living substances, such as toxins, chemicals, drugs, and foreign particles. The immune system recognizes antigens as being foreign to the body and produces antibodies that target the antigens.
|
Review Date:
7/3/2011 Reviewed By: Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.

