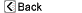Spinal fusion
| Normal anatomy |
The vertebrae are the bones that make up the spinal column, which surrounds and protects the spinal cord. The intervertebral discs are soft tissues that sit between the vertebrae. The discs act as cushions between vertebrae and absorb energy while the spinal column flexes, extends, and twists. Nerves from the spinal cord exit the spinal column between the vertebra.
|
| Indications |
Spinal fusion may be recommended for:
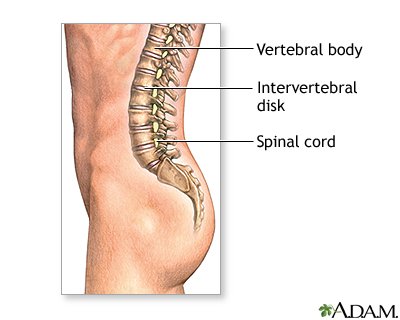
- Abnormal curvature of the spine: (scoliosis or kyphosis)
- Injury to the spinal vertebrae
- Protrusion of the cushioning disc between vertebrae (slipped disc, herniated nucleus pulposus)
- Weak or unstable spine caused by infections or tumors
|
| Incision |
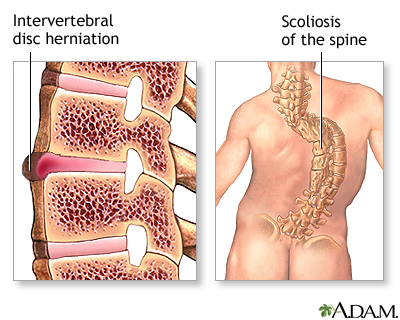
While the patient is deeply asleep and pain-free (using general anesthesia), an incision is made over the spinal area to be treated. Different incisions are made depending on the area to be treated.
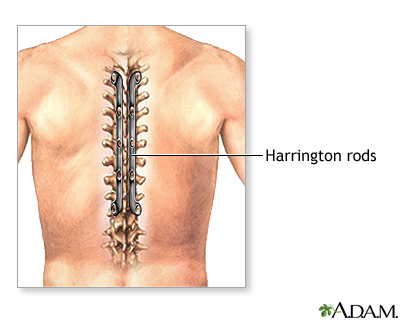
The lower spinal vertebrae are repaired through an incision directly over the spine (posterior lumbar approach). The upper spinal vertebrae are repaired through an incision in the back or side of the neck (cervical spine). The middle spinal vertebrae are repaired through an incision made in the chest and abdomen (anterior thoracic spine). The abnormal or injured vertebrae are repaired and stabilized with bone grafts, metal rods, or both.
|
| Aftercare |
Spinal fusion results in a decreased mobility of the spinal column. Physical therapy is usually necessary post-operatively to optimize recovery and function.
|
|
Review Date:
5/21/2012
Reviewed By:
Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.