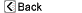Thyroidectomy
| Normal anatomy |
The thyroid gland, a part of the endocrine (hormone ) system, plays a major role in regulating the body's metabolism.
|
| Indications |
Removal of the thyroid may be recommended for:
- Increased thyroid function (hyperthyroidism; thyrotoxicosis)
- Cancer of the thyroid
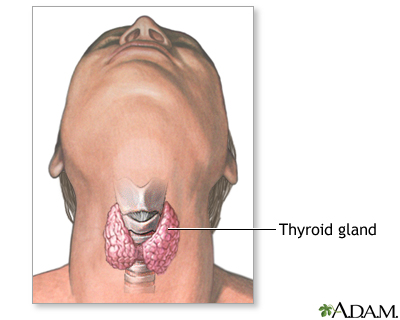
- Enlargement of the thyroid (goiter)
|
| Incision |
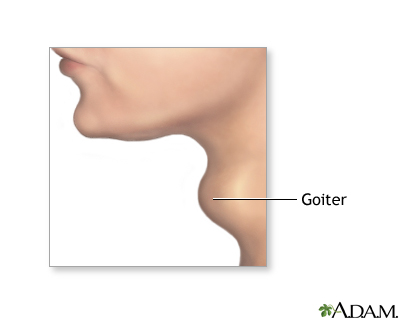
While the patient is deep asleep and pain-free (general anesthesia), an incision is made in the front of the neck.
|
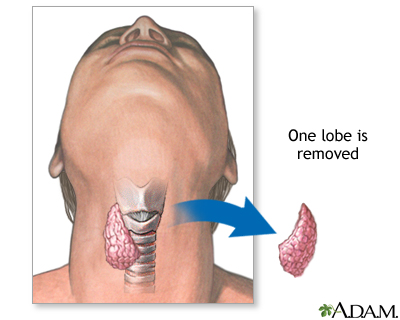
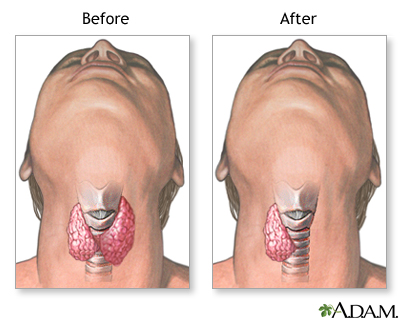
| Procedure |
The thyroid gland is removed. Either one lobe of the thyroid gland, or the entire gland, is removed, depending on the disease process being treated.
|
| Aftercare |
The results of thyroid surgery are usually excellent. Monitoring of thyroid hormone production may continue for some months after the operation. Patients need to take supplemental thyroid hormone for life after complete thyroidectomy.
|
|
Review Date:
12/22/2011
Reviewed By:
Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.