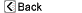Liver transplant
| Normal anatomy |
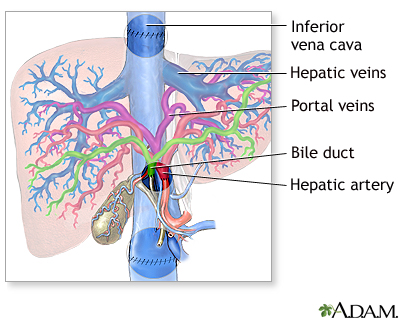
The liver is in the right upper abdomen. The liver serves many functions, including the detoxification of substances delivered by the bloodstream, and the production of many proteins.
|
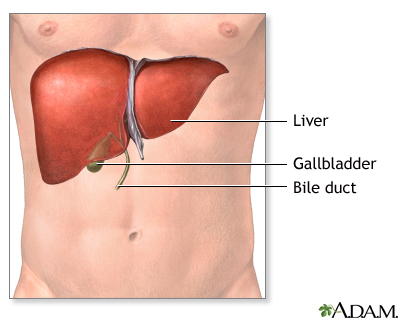
| Indications |
A liver transplant may be recommended for:
- Liver damage due to alcoholism (alcoholic cirrhosis )
- Other forms of end-stage liver disease (such as primary biliary cirrhosis)
- Long-term (chronic) active infection (hepatitis)
- Hepatic (liver) vein clot (thrombosis)
- Birth defects of the liver or bile ducts (biliary atresia)
- Metabolic disorders associated with liver failure (such as Wilson's disease)
|
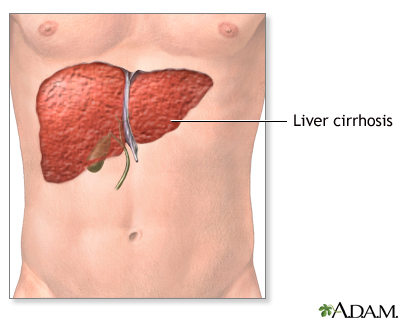
| Incision |
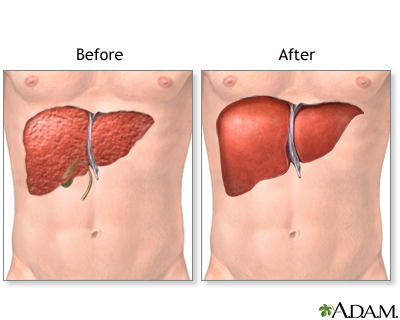
Liver failure causes many problems, including malnutrition, problems with blood clotting, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, and jaundice. Frequently, patients who undergo liver transplantation are quite ill, and require hospitalization in an intensive care unit prior to surgery. A large, upper abdominal transverse incision is used for liver transplant.
|
| Procedure |
Liver transplants are performed in many centers across the country. The healthy liver is obtained from a donor who has not suffered liver injury. The healthy liver is transported in a cooled saline solution that preserves the organ for up to 8 hours. The diseased liver is removed through an incision in the upper abdomen. The new liver is put in place and attached to the patient's blood vessels and bile ducts. The operation can take up to 12 hours and may require blood transfusions.
|
| Aftercare |
Patients require hospital care for 1 - 4 weeks after liver transplant, depending on the degree of illness. After liver transplantation, patients must take immunosuppressive medications for the rest of their lives to prevent immune rejection of the transplanted organ.
|
|
Review Date:
12/22/2011
Reviewed By:
Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.