Macular degeneration
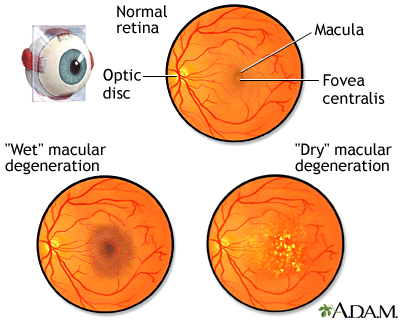
Macular degeneration is a disease of the retina that affects the macula in the back of the eye. The macula is important for clear central vision, allowing an individual to see fine details. There are two types of macular degeneration, dry and wet. Dry macular degeneration is more common and is characterized by the thinning of the retina and drusen, small white deposits that form within the retina. The dry form of macular degeneration is usually mild. Wet macular degeneration can progress more quickly and be more serious. It occurs when vessels under the retinal layer hemorrhage and cause the retinal cells to die, creating blind spots or distorted vision especially in central vision. Special new treatments are available for wet macular degeneration. Both types of macular degernation become increasingly common among people in each succeeding decade over 50.
|
Review Date:
12/26/2011 Reviewed By: Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |

