Esophagus
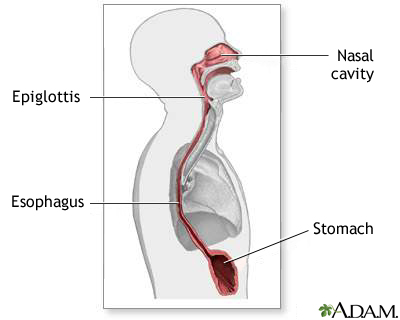
The esophagus connects the mouth with the stomach. The epiglottis closes over the trachea when a swallow occurs to prevent the swallowed substance from being inhaled into the lungs. When a person is unable to swallow because of illness or coma, a tube may be inserted either through the mouth or nose, past the epiglottis, through the esophagus to the stomach. Nutrients will pass through the tube directly into the stomach.
|
Review Date:
5/21/2012 Reviewed By: Harvey Simon, MD, Editor-in-Chief, Associate Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School; Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital. |
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed medical professional should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. © 1997-
A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.

